
Latest News
- Hyundai E&C Becomes Key Player in the Nuclear Decommissioning Market
- Hyundai E&C Accelerates Global Nuclear Expansion into the U.S. Nuclear Market
- Hyundai E&C Shifts into High Gear to Enter Nordic Large-Scale Nuclear Market
- Hyundai E&C Strengthens Korea-Japan Cooperation in Energy Transition and New Growth Businesses
- Hyundai E&C Signals Green Light for Large-Scale Nuclear Power Plant Business in Europe
[Hyundai E&C Encyclopedia vol. 12] The Magic of Reviving Abandoned Land: Soil Remediation Technology
![The Magic of Reviving Abandoned Land: Soil Remediation Technology [Hyundai E&C Encyclopedia vol. 12] The Magic of Reviving Abandoned Land: Soil Remediation Technology](/FileContents/EditorImg/20240725/1.jpg)
Astronomical Value of the Soil Remediation Market
Healthy soil stores large amounts of carbon. Microorganisms in the soil sequester carbon and methane, a greenhouse gas, which is why many experts agree that saving the soil is an effective way to combat climate change. Developed countries are already turning to the soil remediation industry to reduce carbon. According to global market research firm Mordor Intelligence, the global soil remediation market size is expected to reach $41.89 billion in 2023 and grow to $54.78 billion by 2028. This represents a five-year growth rate of 5.51%, which is higher than the global environmental market growth rate of 2.6%.
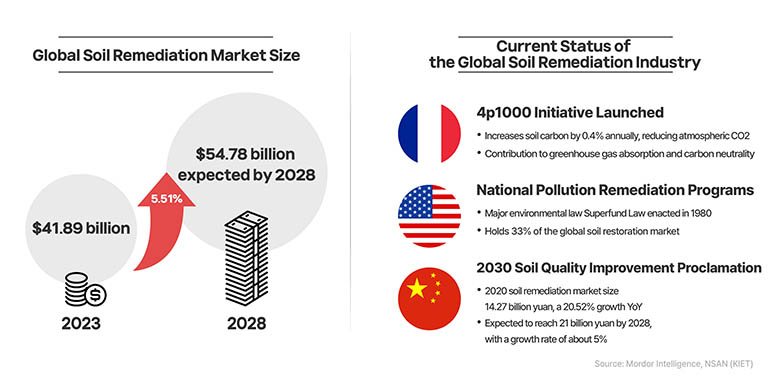
Many countries and companies worldwide are actively engaged in the soil remediation industry. The U.S. set a precedent by enacting the Superfund Law in 1980, which mandates that polluters are responsible for cleaning up their contamination and imposes substantial financial penalties on the polluters. Similarly, France launched the 4P1000 Initiative, aiming to cut atmospheric CO2 by boosting soil carbon content by 0.4% annually. Moreover, China, which holds the world's largest soil remediation market, is making significant investments in soil remediation projects. In 2020, the market for contaminated soil remediation in China was valued at 14.27 billion yuan (2.7 trillion Korean won), reflecting a 20.52% year-on-year growth. This market is projected to grow to 21 billion yuan by 2028, with an annual growth rate of approximately 5%.
The soil remediation industry not only benefits the environment but also generates significant economic value in our evolving world. Although Korea was a latecomer, enacting the Soil Environment Conservation Act in 1995, it has made substantial progress. Starting with the remediation of the maintenance depot site in Munhyeon-district, Busan, in 2001, Korea has been advancing to create a sustainable future through various projects, including military bases and oil storage facilities.
How to Remove Contaminants from Soil?
So how does soil remediation work? In a nutshell, contaminated soil remediation involves removing or “stripping” contaminants from the soil through various methods. The specific technique used depends on the type of contamination and the desired outcome. There are three main types of remediation:

1) Soil-Washing Method: Cleaning Off Just Like Laundry
This process is easy to understand if you think of a washing machine: just like putting contaminated soil and detergent together in a giant washing machine and spinning it, cleaning agents can be used to remove heavy metals, fluoride, low levels of oil, and more from soil on a large scale.
First, just as you would shake off large debris from clothes before putting them in the washing machine, contaminated soil is broken down into fine particles using an air turbulence pipe. Next, the crushed soil is separated into uncontaminated and contaminated particles using a device called a multi-hydrocyclone. This step is similar to how a dryer filter separates large and small dust particles. After that, an acid leaching agent is injected to remove contaminants, akin to adding detergent to a washing machine, where the acid leaching agent chemically reacts with the contaminants to break them down or dissolve them. Finally, just as charcoal is used to purify air, the wastewater generated from the washing process is purified by adsorption and removal with activated carbon. This process is similar to purifying dirty water from a washing machine so it can be reused.
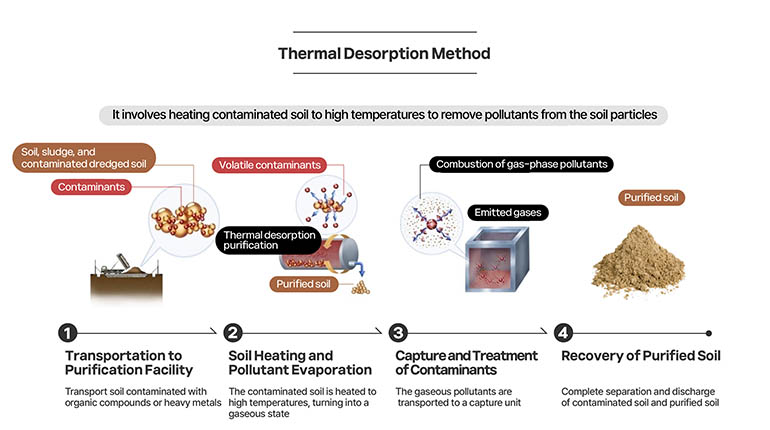
2) Heating to Remove: Thermal Desorption Method
Thermal desorption involves heating soil to high temperatures to volatilize and remove contaminants adsorbed in the soil. This method is particularly effective for large-scale remediation of organic contaminants that are difficult to decompose, such as high concentrations of oil. In addition to its near 100% contaminant removal efficiency, it offers the benefit of recycling waste heat for use in soil drying facilities and allows for the sorting and recycling of the remediated soil.
The thermal desorption process can be compared to using an oven. Soil contaminated with various organic compounds or heavy metals is first placed in a thermal desorption facility, which functions like an oven. The soil is then heated to a consistent high temperature, similar to how food is baked. As the soil heats up, the contaminants evaporate or decompose, turning into a gaseous state, much like water vaporizing during cooking. The next step is “contaminant capture and treatment,” where the gaseous contaminants are directed to a capture unit and safely disposed of using filters or condensers. Finally, just like taking a finished dish out of the oven, the process concludes with the retrieval of the cleaned soil, now free of contaminants due to the thermal desorption process.
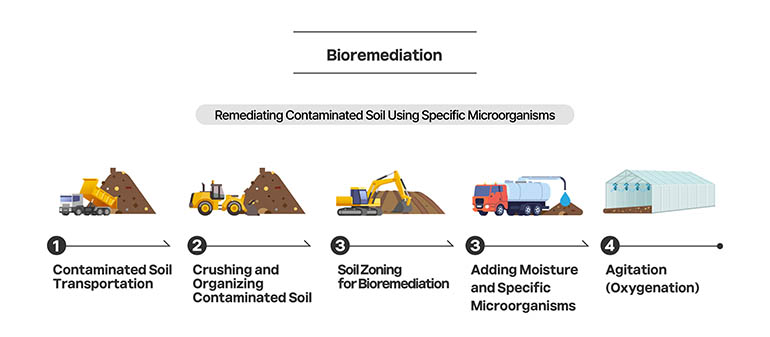
Bioremediation is a method of restoring a contaminated environment to its original state using microorganisms, fungi, plants, or their enzymes. It involves injecting nutrients, moisture, and air into contaminated soil, allowing microorganisms and plants to grow. This process creates an environment where the microorganisms can effectively break down the contaminants in the soil.
First, move the contaminated soil to the designated remediation area. Once there, level the ground by removing stones and weeds, similar to preparing a field for farming. The contaminated soil should be broken down into small particles to create an environment where microorganisms and plants can thrive. Next, divide the contaminated soil into sections, much like dividing a field for planting crops, and select the appropriate microorganisms for each section. Then, add microbes to the soil, hydrating it to help break down the contaminants, just as you would water crops and provide them with fertilizers or nutrients. Finally, introduce oxygen to the soil to support microbial activity, similar to tilling the soil in farming to allow it to breathe.
Hyundai E&C's History of Unmatched Technology Development
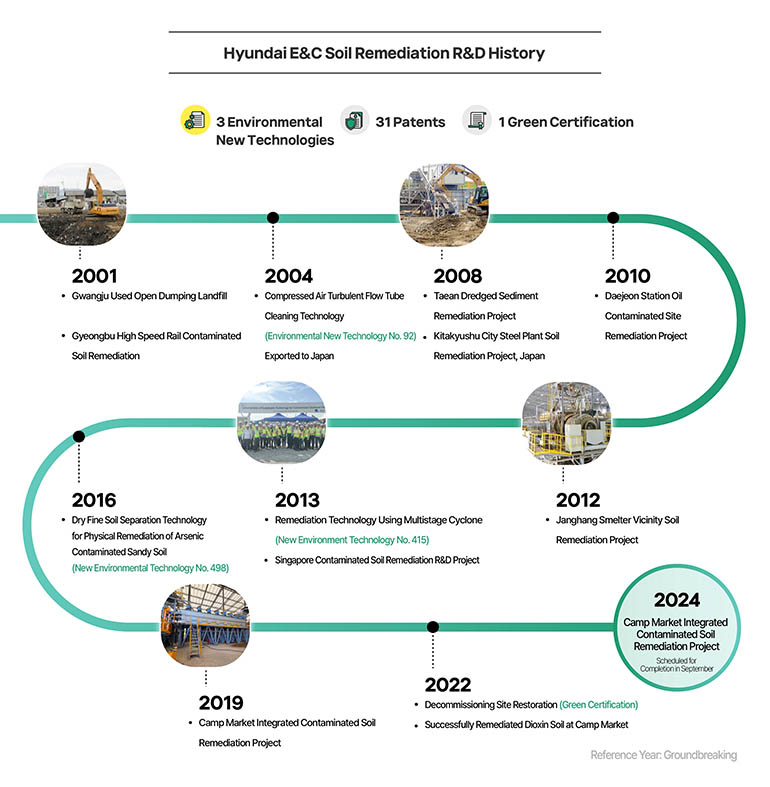
Korea's soil remediation technology has been growing at a rapid pace despite its relatively short history compared to overseas markets such as the U.S., Western Europe, and Japan. Hyundai E&C, in particular, has been leading the market with its outstanding expertise in soil remediation technology. Let's take a look at some of the iconic projects that Hyundai E&C has presented at home and abroad over the past 20 years, from the Gwangju Used Open Dumping Landfill Remediation Project in 2001 to the ongoing Camp Market Complex Contaminated Soil Remediation Project.
Since the days when the soil cleaning business was not active in Korea, Hyundai E&C has been focusing on its own soil cleaning R&D efforts. In particular, the “Compressed Air Turbulent Flow Tube Cleaning Technology” ( New Environmental Technology No. 92), which uses compressed air to separate and remove contaminants from contaminated soil and restore the soil, is a prime example of the company's success in further developing the technology and commercializing it in the field. Hyundai E&C first applied this technology to the “Gwangju Used Open Dumping Landfill Remediation Project” (2001), and then exported the technology to Japan in 2004, gaining international recognition for the technology. Later, the technology was successfully applied to the “Taean Dredged Sediment Remediation Project” (2008) and the “Daejeon Oil Contaminated Site Remediation Project” 2010), proving its competitiveness.
In 2013, Hyundai E&C became the first company in Korea to develop arsenic-contaminated soil remediation technology consisting of a selective soil particle separation method using a multi-stage cyclone and a discharge-free washing method, which once again achieved a feat of being recognized as a new environmental technology (No. 415). This technology minimizes remediation work by precisely separating and removing only specific-sized particles that cause pollution from highly contaminated soil, and it also adsorbs and removes heavy metals extracted from the washing process water, so that even the washing water can be recycled. Hyundai E&C successfully applied this method to the “Janghang Smelter Vicinity Soil Remediation” site, a large-scale soil remediation project.
Hyundai E&C went further to secure “Dry fine soil separation technology for physical purification of arsenic-contaminated sandy soil” in 2016 and “Commercialization technology in the field of nuclear power plant decommissioning site restoration” in 2022. The dry fine soil separation technology, which was first recognized as New Environmental Technology No. 498, is a method of separating soil with high levels of heavy metal contamination using wind without using water and chemicals, and is considered a highly economical technology due to its simple process. In addition, the nuclear power plant site restoration technology, which separates soil contaminated with radioactive substances by particle size and then washes it with potassium chloride (KCl) solution to remove cesium attached to the soil, was the first in Korea to earn green certification in the field of restoring radioactively contaminated soil.
Meanwhile, Hyundai E&C is building a diverse portfolio not only in Korea but also abroad. After participating in a soil remediation project at a steel plant in Kitakyushu City, Japan (2008), the company proposed a contaminated soil remediation R&D project in Singapore in 2013, becoming the first Korean builder to partner with Jurong Town Corporation (JTC) and Nanyang Technological University (NTU). Through this project, Hyundai E&C succeeded in validating the “heavy metal/oil complex contaminated dredged soil remediation technology” in coastal areas, securing the world-class soil remediation technology.
Hyundai Construction's Key Projects Transforming Communities for the Better
1) Transforming a Painful History into a Living Space: The Janghang Smelter Vicinity Soil Remediation Project
The old Janghang Smelter in Seocheon, Chungcheongnam-do, symbolizes both the exploitation of the Japanese colonial era and Korea's industrialization. Built during the Japanese occupation and transitioning through national and private ownership, the smelter was closed in 1989. The surrounding land suffered severe contamination from arsenic, cadmium, and other heavy metals released during the smelting process.

[ (Left) Overview of the soil washing equipment at the Janghang Smelter vicinity soil remediation site. (Right) The input hopper transporting contaminated soil to the equipment ]
In December 2012, Hyundai Construction secured the contract for the first phase of the soil remediation project around the Janghang Smelter. By October 2015, the company had successfully removed contaminants from approximately 72,000㎥ of soil. The project utilized a soil washing method, involving the excavation, washing, and backfilling of the contaminated soil. Hyundai notably employed customized restoration technology tailored to the specific characteristics of the nearby contaminated soil. Observing that smaller soil particles tend to have higher contamination levels, Hyundai developed and implemented a selective particle separation and washing technology specifically for arsenic-contaminated soil, marking a first in Korea. To enhance the absorption of heavy metals, they used specially coated charcoal in the washing process. This innovation also facilitated the 100% recycling of the water used in the washing process, resulting in an environmentally friendly outcome.

[ Janghang Pine Forest, with its blend of pine trees and beautiful beaches, attracts many tourists each year ]
After the remediation project, the vegetation planted to preserve the natural environment has successfully taken root in the nearby pine forest. Together with the surrounding pine trees, it forms a beautiful landscape that attracts about one million visitors each year. Additionally, the restored area around the smelter is being transformed into the nation's first national ecological restoration park. Future plans for this area include the creation of an artificial ecological wetland, serving as a resting place for migratory birds, and a historical center documenting the process of soil contamination and restoration.
2) Creating New Cultural Value for the Region: Camp Market Integrated Contaminated Soil Remediation Project
Located in Bupyeong, Incheon, Camp Market is a former U.S. military base once used for manufacturing, storing, and distributing weapons and ammunition during the Japanese occupation. From 1945 to 1973, it served as a U.S. military base. Incheon city has announced plans to purify the soil on this site and transform it into a major park for the city. Hyundai Construction has been successfully handling the long-awaited Camp Market integrated contaminated soil remediation project for local residents since 2019.
Hyundai E&C succeeded in completely cleaning up 10,031㎥ of dioxin-contaminated soil, one of the main pollutants, around 2022, two years and 11 months after construction began. This marked the first large-scale dioxin remediation in Korea. To safely remove dioxins, Hyundai E&C utilized both the “thermal desorption method” and the “thermal oxidation process.” The thermal desorption method was employed to remove volatile contaminants, while the thermal oxidation process was used to completely eliminate residual contaminants. The thermal oxidation process, in particular, effectively heats the soil to volatilize and remove pollutants, minimizing the impact on both the soil and the surrounding air environment. This complementary use of the two methods resulted in a technically complete cleanup of the dioxin-contaminated soil, reducing the dioxin concentration at the site to 2.18 picograms (1 picogram: 1 trillionth of a gram), well below the target of 100 picograms for the remediation.

[ (Left) View of the soil washing equipment at the “Camp Market Integrated Contaminated Soil Remediation Project site, (Right) Acid leaching tanks used to decompose or dissolve contaminants by adding acid leaching agents ]
Currently, the site has completed the second step of the main remediation process, which involves cleaning oil and heavy metal-contaminated soil. This area covers 169,976㎥, and Hyundai E&C used the “soil washing method,” which is effective for this type of contamination. The site was safely remediated using its own soil washing facility, equipped with dry magnetic screening, trommel screen, wet magnetic screening, hydrocyclone (multi-stage granularity sifter), and concentration tank for physical cleaning. Additionally, the facility includes acid elution tanks, wet dehydration equipment, and neutralization tanks for chemical cleaning.

[ (Left) Panorama of the “Camp Market Integrated Contaminated Soil Remediation Project” site after the cleanup, (Right) View of the site in 2021 during the ongoing construction ]
To prevent noise and fine dust generated during the soil cleaning process, Hyundai E&C took great care in managing worker safety and the working environment, including gas masks, dust-proof suits, and watering facilities. In particular, given that the site is a densely populated residential area surrounded by apartments, the company managed emissions generated during the soil cleaning process within legal standards and responded to local needs by installing additional CCTV cameras. In addition, during the construction period, the Korean builder held numerous briefings with the Ministry of National Defense, the Korea Environment Agency, professors from the Korean Society of Soil and Groundwater Environment, Incheon Metropolitan City, Bupyeong-gu Office, NGOs, and local residents, and appointed apartment residents as honorary supervisors to ensure safe and transparent management of the site. Currently, the site is wrapping up all construction work and is scheduled for completion in September. Hyundai E&C plans to build on its know-how and technology in contaminated soil remediation from Camp Market to win additional projects such as the US Army Camp Red Cloud and Seongnam Golf Course.
In recent years, contaminated soil remediation technology has been rapidly advancing. The applications of soil monitoring technology utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, including machine learning, are also gradually expanding. Contaminated soil remediation technology is a truly futuristic industry that not only improves the quality of our lives but also creates new economic and cultural values. Hyundai E&C, which is already active in the U.S. nuclear decommissioning market, plans to introduce commercialized soil restoration technology in the nuclear decommissioning site restoration business, which is expected to become a significant blue ocean market. Please stay tuned to Hyundai E&C's ongoing efforts to develop proprietary soil remediation technologies and build a strong soil remediation portfolio, all with the aim of fostering a sustainable ecosystem.

